
Introduction to EU REACH SVHC Compliance
What is the EU reach regulation?
REACH stands for "Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of CheMICals".
This EU regULation aims to:
- Protect consumers from harmful synthetic chemicals known to pose risks to human health.
- Enhance the competitiveness of companies prioritizing consumer safety.
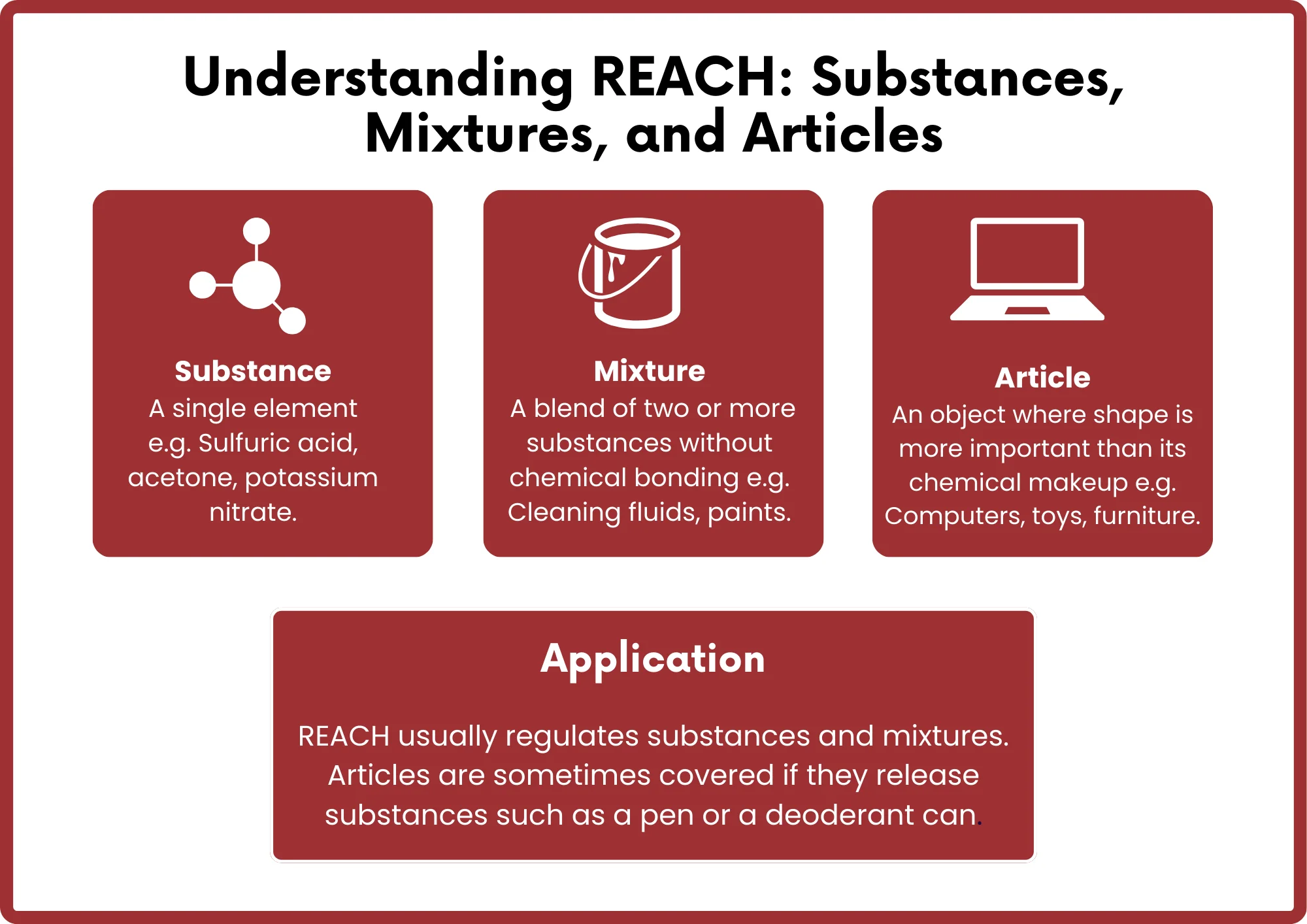
The REACH regulation applies to nearly all types of products, ranging from industrial goods to personal items. Any substance manufactuRED in or imported into the EU market in quantities above a specified threshold must be registered with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
This document outlines the compliance requirements of the EU REACH regulation to help ensure your products can be legally sold in the EU market.
Who Must Register with the European Chemicals Agency?
Entities meeting the following conditions are generally required to register:
1. Manufacturers
Companies producing chemical substances within the European Economic Area (EEA) must register these substances, including:
- Individual chemicals.
- Substances intentionally released from mixtures or articles under normal or reasonably foreseeable use conditions.
2. Importers
Companies importing one tonne or more of chemical substances annually into the EEA must register these substances, including:
- Individual chemicals.
- Chemicals contained in mixtures or articles.
3. Only Representatives (OR)
Non-EEA manufacturers can designate an Only Representative (OR) based in the EEA to fulfill registration obligations on their behalf.
> Note: Once a substance is registered via an OR, other domestic importers are classified as "downstream users" and do not need to register it again.
Understanding the EU REACH Framework
The regulation categorizes chemical substances into three key lists:
1. Candidate List of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC)
- Includes substances identified as harmful to human health or the environment, such as carcinogenic, mutagenic, toxic for reproduction (CMR), persistent, or bioaccumulative substances.
- Listing on the Candidate List is the first step toward possible authorization or restriction.
2. Authorization List (Annex XIV)
- Contains substances from the Candidate List that require explicit authorization for use.
- Companies must demonstrate that risks are adequately controlled or that socio-economic benefits outweigh the risks to gain authorization.
3. Restriction List (Annex XVII)
- Includes substances restricted or banned within the EU for specific uses, production, or sale.
Dynamic Updates: These lists are regularly updated based on emerging scientific information or additional regulatory needs to encourage the use of safer alternatives.
How to Comply with the EU REACH Regulation
Manufacturers and importers must submit a registration dossier that includes:
- Substance properties, safety use information, and risk management measures.
Key Steps
Step 1: Determine Exemption Eligibility
Certain substances are exempt from registration under the following circumstances:
- Manufactured or imported in quantities below one tonne annually.
- Used for research and development (R&D).
- Classified as waste.
- Covered by other EU legislation (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food).
- Pesticides, biocides, and chemicals in polymers.
Step 2: Inventory of Chemicals
Identify the chemicals in your products and cross-check against the following lists:
1. Restriction List (Annex XVII): Registration is required for restricted substances if quantities exceed one tonne annually.
2. Authorization List (Annex XIV): Application is required for substances requiring explicit authorization.
3. Candidate List (SVHC): Prepare for potential restrictions by identifying chemicals that may impact your supply chain.
Step 3: Submit a Substance Inquiry Dossier
For chemicals exceeding one tonne annually listed in Annex XVII, submit a dossier to ECHA. This process informs ECHA of your intent to register and facilitates collaboration among registrants.
Step 4: Joint or Individual Registration
- If other registrants exist, appoint a lead registrant to submit the application first, followed by others.
- If no other registrants exist, you must independently compile and submit your dossier.
Third-Party Testing: Companies uncertain about the chemicals in their products should consider third-party testing to ensure compliance.
Risks of Non-Compliance with REACH
- Legal Consequences: Potential restrictions on substance production or importation and significant financial penalties.
- Economic Risks: Fines can reach hundreds of thousands of euros for non-compliance.
High-risk scenarios include:
- Sudden production increases due to surging demand.
- Sales impacted by political or socio-economic changes, especially within the EU.
- Opaque supply chains, particularly involving Chinese components.
Benefits of EU reach compliance
While REACH compliance may seem daunting, it offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced quality control across supply chains.
- Elimination of harmful chemicals from products.
- Reduced regulatory risks.
- Access to the entire European market.
- Promotion of environmentally and health-conscious practices to customers.
JJR LAB provides REACH compliance testing services to support your ECHA registration requirements and ensure your products meet EU standards.
For questions or further assistance, contact JJR LAB. We can help you determine the conditions for registering your products under the EU REACH regulation!
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
 What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
 Australia IoT Security Compliance
Australia IoT Security Compliance
 V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
 Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
 FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
 What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
 What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




