
Guide to Obtaining the Korea KC Certification
Overview
On August 25, 2008, South Korea’s Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) announced that the National Standards Committee woULd implement a new unified national certification mark—the KC (Korea Certification) mark—from July 2009 to December 2010.
kc certification is a mandatory safety certification system for electrical and electronic products, implemented by the Korea Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) under the *Electric Appliances Safety Control Act*, effective from January 1, 2009.
To avoid duplicated certification efforts, starting July 1, 2012, EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) and Safety are managed separately. Products must obtain both KC (Safety) and KCC (EMC/MSIP) certifications as applicable.
Designated issuing and testing organizations:
* Korea Testing Certification (KTC)
* Korea Electrical Testing Institute (KTL)
1. Categories of KC Certification
1.1 Certification Types
KC Certification includes:
* KC Safety
* KC EMC and RF
* MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standards)
KC Safety certification is divided into three levels based on the product's risk classification:
* Compulsory Safety Certification: RequiRED for high-risk products. Annual factory audits apply.
* Self-Regulated Safety Confirmation: Valid for 5 years.
* Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity: No certificate issued; the declaration remains permanently valid.
1.2 Certification Holder Requirements
* Compulsory certification must be held by the manufacturer (factory).
* The other two types may be held by the manufacturer, importer, or supplier.
1.3 Factory Inspection
* Required for Compulsory Safety Certification (initial and annual audits).
* Not required for the other two certification types.
2. KC EMC and RF Certification
This covers:
* Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
* Radio frequency (RF)
* Telecommunications testing
Purpose:
* Ensure the product operates properly in its electromagnetic environment (EMS).
* Ensure the product doesn’t excessively interfere with other devices (EMI).
Under the *Radio Waves Act*, certification types are:
* Certification of Conformity
* Registration of Compatibility
* Interim Certification
3. MEPS: Energy Efficiency Labeling
MEPS labeling indicates the energy efficiency level of a product. It aims to help consumers make informed decisions and encourages the selection of energy-saving products.
4. Applicable Product Range
KC Certification applies to electrical products with AC voltage between 50V and 1000V.
Examples of Product Categories:
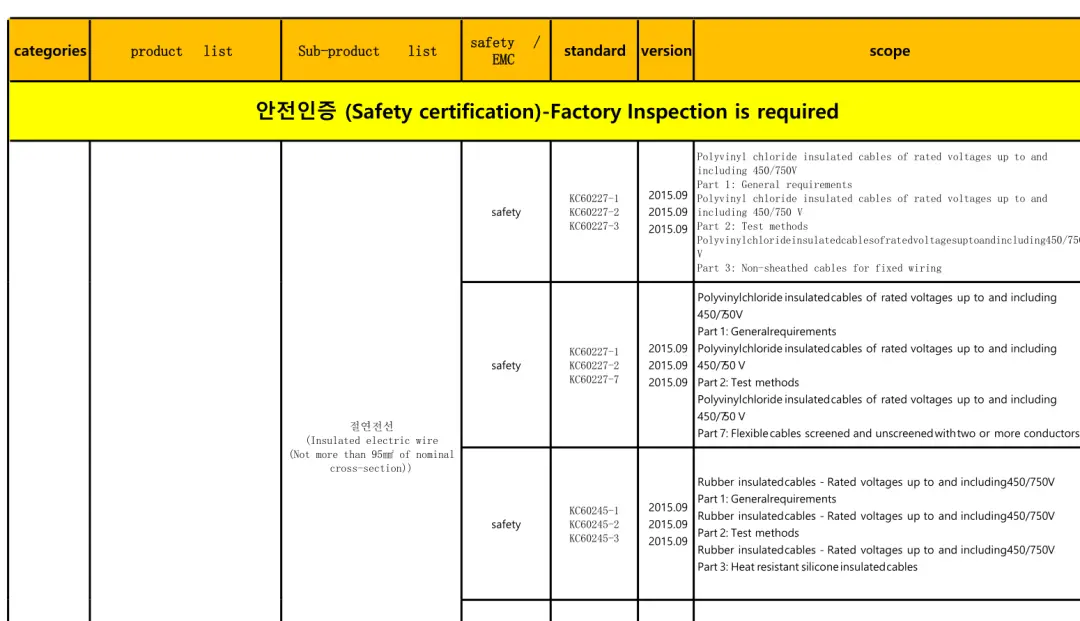
(A) Safety-Certified Products (57 types)
* Electric wires and cables
* Electrical switches
* Capacitors and power filters
* Electrical components and connectors
* Electrical protective devices
* Household insulated transformers
* Household appliances
* Power tools
* AV equipment
* IT and office equipment
* Lighting equipment
(B) Self-Regulated Safety Confirmation Products (95 types)
* Electrical switches
* Household insulated transformers
* Household appliances
* AV equipment
* IT and office equipment
* Lighting equipment
5. KC Certification Process
1. Submit product samples and documents to the testing agency.
2. The agency sends materials to KTC/KTL for testing.
3. KTC/KTL conducts safety testing and issues a kc test report.
4. For compulsory certifications, KTC/KTL conducts a factory audit.
5. Upon approval, the kc certificate is issued.
6. Required Documents
* Application form
* Product label
* Korean-language user manual
* Component list
* List of derivative models
* Circuit diagrams and layout
* Certificates for key components
* Specifications for transformers, inductors, etc.
* cb certificate and report (if available)
7. KC vs. kcc certification
* KCC Certification applies to IT, telecom, and RF wireless products.
* Includes EMC, telecom, and RF testing.
* Issued by the Radio Research Agency (RRA) under the Korea Communications Commission (KCC).
Note:
As of January 1, 2011, the original KCC logo has been unified into the KC logo system. However, for KCC-certified products, the KC logo includes a KCC ID number beneath it.
8. KC Labeling Requirements
The product label must include the following:
1. KC mark with certificate number (e.g., SUxxxxxxxx)
2. Product name (in Korean)
3. Model number
4. Voltage and frequency
5. Manufacturer’s name
6. Country of origin
7. Double insulation symbol (if applicable)
8. Date of manufacture
9. After-sales service phone number (must be in Korea)
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 How Do You Get a CE Mark
How Do You Get a CE Mark
 IEC 60529 IP Rating Ingress Protection Standard
IEC 60529 IP Rating Ingress Protection Standard
 IEC 60601-1 Medical Electrical Equipment Basic Saf
IEC 60601-1 Medical Electrical Equipment Basic Saf
 European Authorized Representative Medical Devices
European Authorized Representative Medical Devices
 EU Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Direc
EU Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Direc
 How to Get CE Approval
How to Get CE Approval
 Accelerated Ageing Test
Accelerated Ageing Test
 IP Ingress Protection Testing
IP Ingress Protection Testing
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




