
Hemocompatibility Testing ISO 10993
ISO 10993-4:2017 Interpretation of Hemocompatibility Testing Standards
Medical devices that come into direct or indirect contact with human circULating blood must undergo hemocompatibility testing if there is insufficient data to demonstrate compliance with blood compatibility requirements. iso 10993-4:2017 is a key reference standard for such tests. Today, China's JJR Laboratory will interpret the requirements of this standard and explore the testing protocols.
Overview of Hemocompatibility Testing
Hemocompatibility testing evaluates the effects of medical devices or materials in contact with blood or blood products. When selecting and designing test protocols, factors such as product design, clinical use, environment, and risk-benefit analysis should be consideRED.
ISO 10993-4:2017, as an essential reference, primarily includes three components:
1. Classification of blood-contacting medical devices.
2. Fundamental characteristics for assessing blood responses.
3. Selection of test methods.
Classification of Blood-Contacting Devices
Non-blood-contact devices refer to those that do not directly or indirectly interact with blood that remains in or is returned to the body, such as in vitro diagnostic reagents and blood collection tubes.
External communicating devices generally interact with circulating blood and connect to the human vascular system. Examples include blood collection devices, catheters, blood storage or transport equipment like blood bags and transfusion tubing, vascular catheters, and intravenous extensions. Other examples include atherectomy devices, blood monitoring systems, cardiopulmonary bypass circuits, therapeutic blood separation equipment, extracorporeal membrane oxygenators, dialysis devices, cardiac interventional devices, and vascular guidewires.
Implantable devices involve prolonged contact with blood and include annuloplasty rings, arteriovenous shunts, implantable monitors, ventricular assist devices, artificial hearts, embolization devices, synthetic vascular grafts, implantable defibrillators, pacemaker leads, stents, and similar products.
Blood Reaction Characteristics
After identifying the device category, it is essential to understand the blood reaction characteristics of the product to select appropriate test methods. Two critical points should be noted:
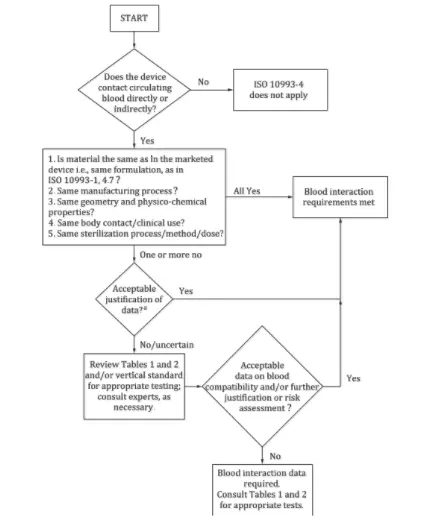
- The standard provides a decision flowchart to determine whether hemocompatibility testing is necessary.
- The standard lists device examples with corresponding test categories.
Answering the following four questions can help determine whether hemocompatibility testing is required:
1. Does the device directly or indirectly contact circulating blood? If not, this standard does not apply; if yes, proceed to the next question.
2. Do the device materials match those of marketed products in terms of processing, structure, physicocheMICal properties, sterilization methods, and clinical usage? If all match, no testing is needed; otherwise, proceed further.
3. Can differences be evaluated and found acceptable? If yes, testing is unnecessary; if not, further risk evaluation is needed.
4. Is the risk assessment data on blood compatibility acceptable? If yes, testing is unnecessary; otherwise, testing is required according to relevant guidelines.
Examples of devices requiring testing include blood monitoring devices, which may require hemolysis, coagulation, platelet activation, and hematology tests.
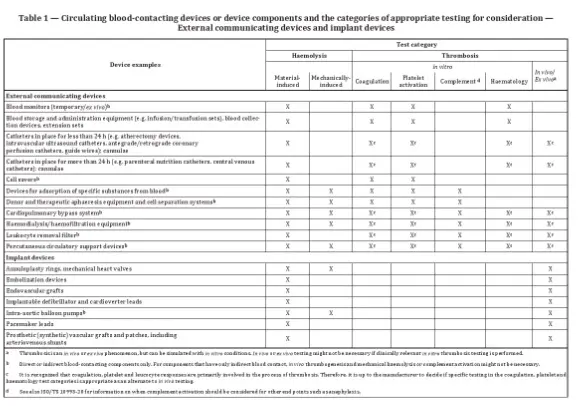
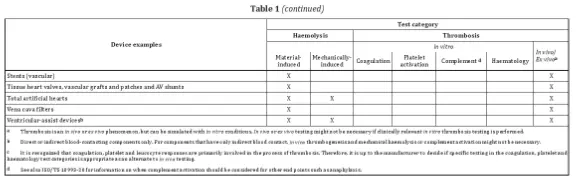
Parameters to consider include the structural design, physicochemical properties, surface characteristics, sterilization conditions, duration of contact, temperature, and blood flow or anticoagulation conditions. For implantable products, testing should closely simulate clinical conditions.
Description of Testing Methods
Generally, hemocompatibility testing includes two main categories:
1. Hemolysis Tests: These may be material-mediated or mechanically mediated.
2. Thrombosis Tests: These include in vitro tests for coagulation, platelet activation, and complement activation, as well as in vivo and ex vivo tests.
Key considerations for in vitro tests include hematocrit, anticoagulant type and dosage, blood sample preparation, temperature, pH, flow conditions, and blood/surface area ratios.
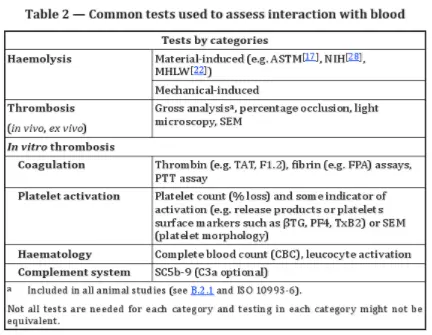
Ex vivo tests are essential for extracorporeal devices like dialysis systems. These tests can monitor platelet adhesion, thrombus formation, and fibrinogen deposition. Real-time blood flow changes can indicate thrombus deposition and embolization.
For implantable devices like vascular stents, in vivo animal studies should simulate clinical conditions. Key evaluation criteria include device patency and histopathological assessment after removal. Advanced techniques such as angiography or intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) may also be used.
Conclusion
ISO 10993-4:2017 outlines the classification of blood-contacting medical devices, fundamental blood reaction characteristics, and standard testing methods. However, detailed guidance on test designs, such as in vivo thrombosis or platelet activation assays, requires consulting Annexes A-G of the standard.
References
[1] ISO 10993-4:2017 Biological evaluation of medical devices -- Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 RCM AS/NZS CISPR 32:2023 Testing for Power Adapte
RCM AS/NZS CISPR 32:2023 Testing for Power Adapte
 How to get Australia SAA Compliance?
How to get Australia SAA Compliance?
 Does Canada Require RoHS Compliance
Does Canada Require RoHS Compliance
 EU CE LVD, EMC, RoHS Directives Compliance Guide
EU CE LVD, EMC, RoHS Directives Compliance Guide
 Quick Guide to the CE-LVD Low Voltage Directive
Quick Guide to the CE-LVD Low Voltage Directive
 Global Certification Guide for Lithium Batteries
Global Certification Guide for Lithium Batteries
 Compliance of Amazon 18650 Lithium Battery Product
Compliance of Amazon 18650 Lithium Battery Product
 What is CE Certification and EU Authorized Represe
What is CE Certification and EU Authorized Represe
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




