
Compliance Testing for EU Food Contact Materials Regulations
RegULation (EC) No 1935/2004 serves as the framework regulation for EU food contact materials. It does not directly specify detailed testing items; instead, it establishes general requirements and the principle of authorizing the formulation of specific measures. Specific testing requirements are mainly stipulated in separate measures targeting particular materials (e.g., EU regulations and directives) or in line with unified standards recognized by EU member states.
Based on the framework principles of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and the specific measures issued thereunder, food contact materials typically require four types of tests as follows:
Overall Migration Test
It aims to assess the total amount of all non-volatile substances migrating from the material into food.
① Standard Testing Method: Immerse the material in food simulants (e.g., distilled water, 3% acetic acid, 10% ethanol, isooctane, etc., selected according to food types) under specific temperature and time conditions, then evaporate the simulant and weigh the residue.
② Limit Value: Generally 10 mg/dm² (based on the food contact area) or 60 mg/kg. Stricter requirements apply to specific containers or products for infants and young children.
③ Compliance Standard: Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 (for plastics) and its amendments are the core basis, which specify detailed testing conditions.
Specific Migration Test
It is designed to measure the migration amount of certain specific hazardous substances (usually monomers, additives, heavy metals, etc.) into food.
Common Tested Substances
① Heavy metals: Lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium (VI), etc.
② Monomers/starting materials: Such as vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile, BISphenol A (BPA), formaldehyde in plastics, etc.
③ Additives: Plasticizers (e.g., phthalates), antioxidants, stabilizers, etc.
④ Testing Method: After immersion in food simulants, conduct quantitative analysis using precision instruments (e.g., GC-MS, HPLC, ICP-MS).
⑤ Limit Value: Each substance has a clear Specific Migration Limit (SML) specified in relevant regulations. For example, the SML of BPA is 0.05 mg/kg.
Sensory Test
It ensures that the material will not transfer its odor or taste to food, thus avoiding adverse effects on food quality.
① Migration-based Testing: Immerse the material in food simulants (e.g., water or alcohol solution), then a panel of trained reviewers evaluates the soaking solution through smelling and tasting.
② Material Odor Test: Directly assess the odor released by the material under specific conditions.
③ Compliance Standard: Often refers to the sensory requirements of the German LFGB regulation or relevant EU standards.
Material Composition and Compliance Analysis
It verifies whether the material meets the requirements of positive lists and identifies potential hazardous substances.
① Screening Analysis: Use technologies such as FTIR, GC-MS, and PY-GC-MS to screen for unknown substances in materials or verify their compliance with positive lists (e.g., the authorized list of monomers and additives in the Plastic Regulation (EU) 10/2011).
② Total Heavy Metal Content Test: Determine the total content of heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium, mercury, hexavalent chromium) in the material itself (different from migration amount), with clear limit values specified.
③ Primary Aromatic Amine Test: A specific test for materials such as polyamides that may produce carcinogenic aromatic amines.
Key References to Specific Regulations
The specific selection, methods, and limit values of testing items are mainly based on EU regulations targeting specific materials:
① Plastics: (EU) No 10/2011 (and its series of amendments) is the most comprehensive and core regulation, specifying detailed migration test conditions, simulant selection, lists of specific substances, and their limit values.
② Recycled Plastics: (EU) 2022/1616 stipulates more stringent testing and certification requirements.
③ CeraMICs: Directive 84/500/EEC and its amendments, focusing mainly on the migration of lead and cadmium.
④ Active and Intelligent Materials: Specifically regulated by (EC) No 450/2009.
⑤ Member State Regulations: For materials without unified EU regulations (e.g., paper and cardboard, rubber, silica gel, coatings, etc.), compliance shall be in accordance with the requirements of major member states’ regulations (e.g., German LFGB, French DGCCRF, Italian and Dutch regulations), which usually include specific testing lists.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 What is Protection Class EN 60529?
What is Protection Class EN 60529?
 IP69 Certified Protection
IP69 Certified Protection
 California Energy Commission Testing Lab
California Energy Commission Testing Lab
 What Does the Canadian IC Mark Mean?
What Does the Canadian IC Mark Mean?
 How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification cost?
How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification cost?
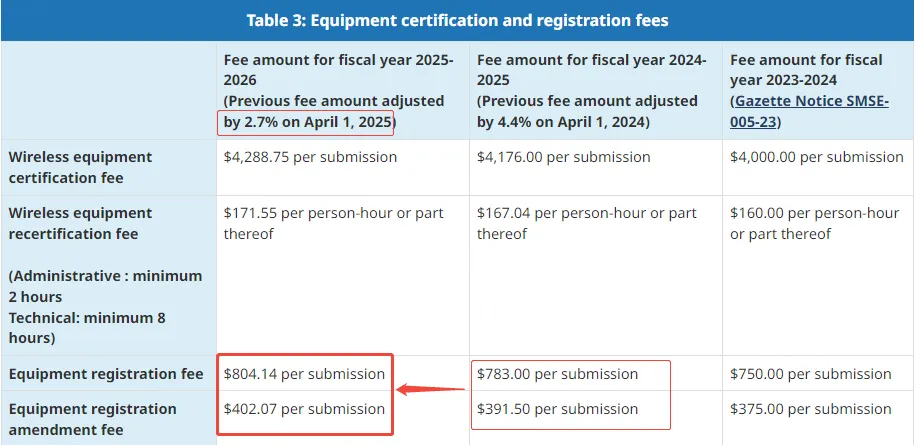 How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification Fee?
How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification Fee?
 How Much is the UL 982 Test Report csost?
How Much is the UL 982 Test Report csost?
 ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Test Laboratory
ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Test Laboratory
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




