
Does Your Product Require FCC ID or SDoC?
FCC (Federal Communications Commission) is the U.S. federal regULatory body for communications. Products subject to FCC certification include radio frequency (RF) devices, communication products, and digital products. All such products must obtain fcc approval (i.e., pass FCC certification) to enter the U.S. market.

FCC certification is divided into two types: fcc sdoc and fcc id
(1) FCC sdoc applies to conventional electrical and electronic products without wireless RF technology, such as:
① Computer monitors, printers
② Household appliances (except microwave ovens, which have special regulations)
③ Power tools, digital cameras
④ USB devices, HDMI cables, etc.
(2) FCC ID is a mandatory certification for wireless products entering the U.S. market. All wireless products must be tested in accordance with regulations by an accREDited laboratory (e.g., A2LA-accredited labs, which only hold testing and report-issuing qualifications, not certification issuance authority) and obtain certification from a Telecommunication Certification Body (TCB).
(3) Wireless products/equipment refer to devices with wireless technology, including:
① Laptops, mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers
② Bluetooth devices (headphones, speakers)
③ Walkie-talkies, broadcast transmitters
④ Any device with communication functions such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth (e.g., smart home devices, IoT devices)
Common Wireless Technologies for Wireless Product Certification
Bluetooth technology is mainly divided into two categories: Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which differ significantly in application scenarios, power consumption, and transmission rates.
(1) Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR)
· Version: Typically BT2.0/3.0
· Frequency band: 2.4GHz ISM band
· Features: Supports point-to-point communication; suitable for audio transmission (e.g., headphones, speakers) and data transmission (e.g., mobile printing)
(2) Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
· Version: Typically BT4.0 or higher
· Frequency band: 2.4GHz ISM band
· Features: Ultra-low power consumption; supports broadcasting, Mesh networks, and device positioning; suitable for IoT, health monitoring, and other scenarios
(3) Single-mode Bluetooth
· Supports either Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR) or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) alone; also referred to as single-mode BT or single-mode BLE
(4) Dual-mode Bluetooth
· Supports both Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) simultaneously
Note: BT and BLE are two distinct technologies with significantly different testing methods and content, requiring separate test reports.
what is an fcc id Number?
An fcc id number is a certification mark for wireless products. The FCC reviews the application materials and test data submitted by the applicant; if the product meets FCC requirements for wireless devices, an FCC ID number is granted. The device must permanently display its unique FCC ID.
· Typical format: FCC ID: AAAAA-BBBBBBB
① AAAAA: Applicant code, randomly assigned by the FCC (currently 5 characters)
② BBBBBBB: Product code
FCC ID Certification Process
① Provide samples (operational prototype + fixed-frequency prototype) and application materials
② Conduct testing in accordance with regulations
③ JJR Laboratory (China) issues the test report
④ Sign and return confidential documents
⑤ Submit certification materials
⑥ TCB reviews the materials
⑦ Upload data and obtain certification
(FAQs) About FCC ID for Customers
(1) Question: Series application: If products belong to the same series but have slightly different PCBs or component parameters, can they be certified together?
Response: It depends on the specific situation. If the differences affect RF performance (e.g., different wiring from the chip to the antenna), joint certification is not allowed. (Note: For products to be listed on TEMU, the requirement for "same model with different colors" is more stringent; this must be considered for TEMU platform entry.)
(2) Question: Can products with different power supplies be certified together?
Response: If only the power supply differs, supplementary difference testing is required.
(3) Question: Is a U.S. agent required for each FCC ID application?
Response: Yes, a U.S. agent agreement is required for each individual FCC ID. Therefore, a new U.S. agent agreement must be signed for each new project and each new FCC ID issued.
(4) Question: Are two fixed-frequency prototypes mandatory?
Response: Two fixed-frequency prototypes are required for formal certification. However, if providing two prototypes is not feasible, you may submit:
① One fixed-frequency prototype with an SMA cable soldered for conducted testing; or
② One prototype for radiated testing (without an SMA cable soldered), with the customer’s cooperation for on-site SMA cable soldering by our laboratory.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 What is Protection Class EN 60529?
What is Protection Class EN 60529?
 IP69 Certified Protection
IP69 Certified Protection
 California Energy Commission Testing Lab
California Energy Commission Testing Lab
 What Does the Canadian IC Mark Mean?
What Does the Canadian IC Mark Mean?
 How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification cost?
How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification cost?
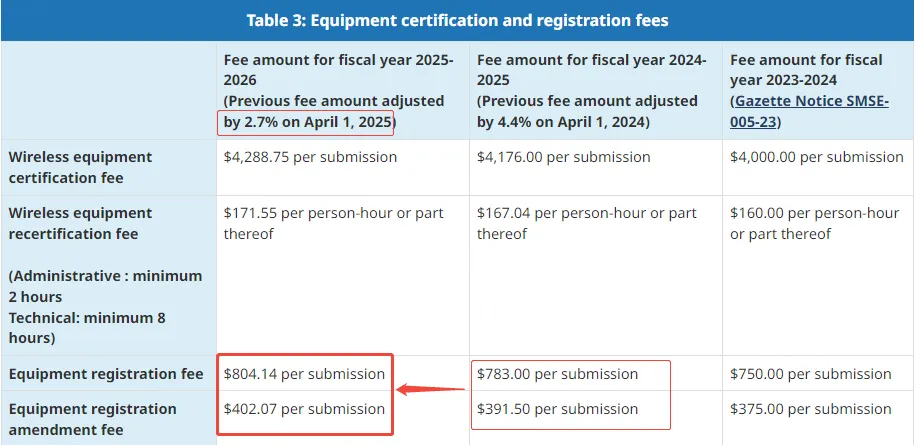 How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification Fee?
How Much is the Canada IC ID Certification Fee?
 How Much is the UL 982 Test Report csost?
How Much is the UL 982 Test Report csost?
 ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Test Laboratory
ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Test Laboratory
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




