
What is the ANSI C136.31-2023 Testing Standard?
Latest Standard | National Standard for Roadway and Area Lighting Fixtures in the U.S. – Vibration NEMA ANSI C136.31-2023 Standard Interpretation
1. Test Scope:
This standard covers the minimum vibration resistance and vibration testing methods for roadway and area lighting fixtures. It does not apply to natural or catastrophic disasters.
2. Vibration Impact on Roadway and Area Lighting in Actual Use:
a. Vibration caused by wind.
b. Vibration caused by passing vehicles.
3. Test Methods:
3.1 Resonant Frequency Search:
- Frequency Range (Hz): 2-30
- Acceleration (g): 0.2
- Sweep Rate (oct/min): 1
- Test Axes: X, Y, Z
In other words: Within the frequency range of 2-30 Hz, with an acceleration of 0.2 g and a sweep rate of 1 octave per minute, the resonant frequencies of the fixture in the three axes (X/Y/Z) are measuRED. The most severe frequency is then used for the durability test (resonant frequency).
3.2 Fixed Frequency Durability Test:
- Test Frequency: The resonant frequency measured in 3.1; if no resonant frequency is found, 30 Hz is used.
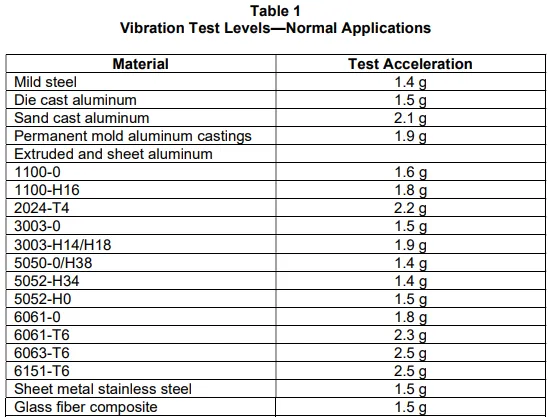
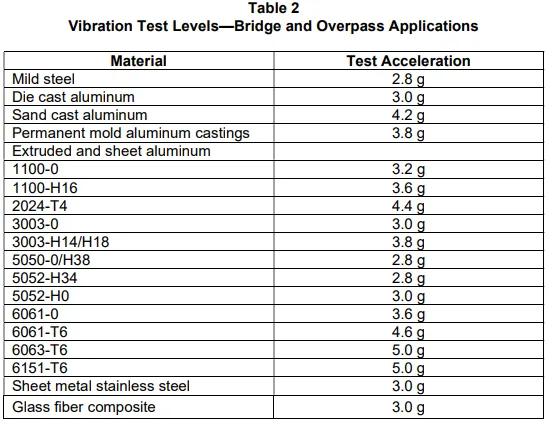
- Acceleration: Select from Table 1/Table 2, typically 3 g.
- Number of Tests: 100,000 cycles.
Test Time: T = N / 60f, where N is the number of tests and f is the test frequency.
For example: If the resonant frequency is measured as 6.95 Hz, then the test time T = 4 hours.
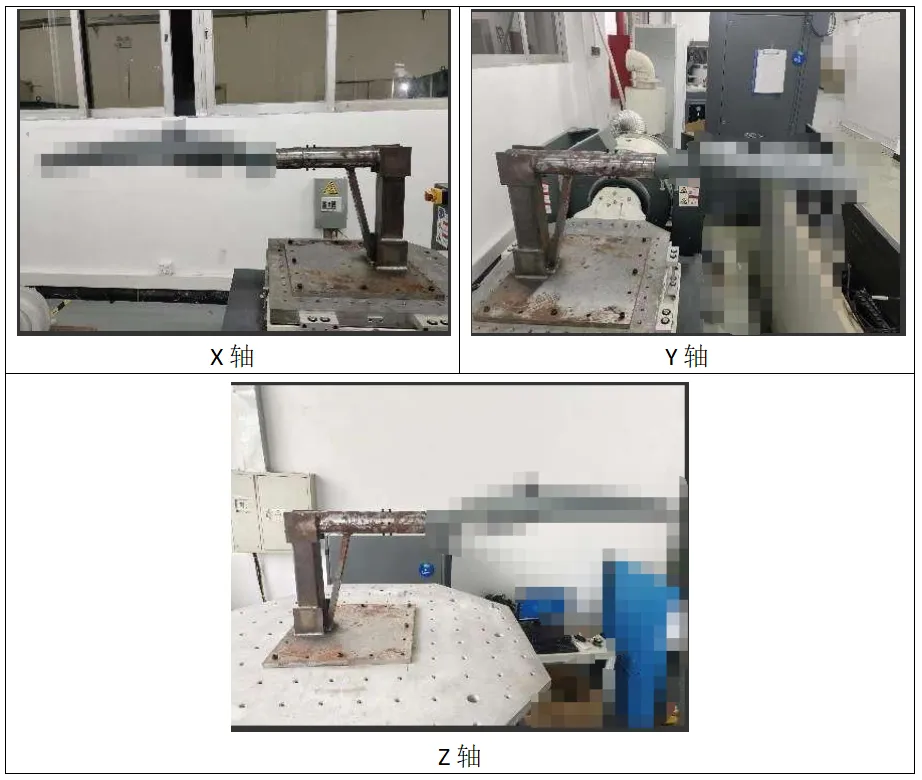
4. Practical Case:
(The image below shows a dedicated fixture for street lights, simULating the actual installation state.)
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
 What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
 Australia IoT Security Compliance
Australia IoT Security Compliance
 V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
 Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
 FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
 What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
 What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




