
Chemical Testing for RoHS Ten Substances
What is RoHS?
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is a mandatory standard established by the European Union. Its fULl name is the "Directive on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment." The directive primarily regulates the materials and manufacturing processes of electronic and electrical products, ensuring they are more beneficial for human health and environmental protection.

RoHS Ten Substances
ROHS Testing covers the following ten hazardous substances:
- Lead (Pb)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Mercury (Hg)
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI)
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBBs)
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs)
- Diisobutyl Phthalate (DIBP)
- Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP)
- Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP)
Scope of rohs testing
RoHS testing applies to:
- Electrical and electronic equipment
- Components
- Various raw materials
Importance of RoHS Testing
The RoHS directive sets limits on these ten hazardous substances to protect the environment and human health. Compliance with RoHS is essential for electronic and electrical product manufacturers and suppliers as it:
- Enhances market competitiveness
- Meets consumer demand for eco-friendly products
Maximum Allowable Concentrations of RoHS Substances
1. Lead (Pb): A toxic metal commonly found in solder, glass, and PVC stabilizers. The allowable limit in RoHS testing is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
2. Cadmium (Cd): A toxic metal used in switches, springs, connectors, housings, PCB, and batteries. The allowable limit is ≤100 ppm (0.01%).
3. Mercury (Hg): Found in thermostats, sensors, switches, and light bulbs. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
4. Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI): A toxic cheMICal mainly used in metal corrosion-resistant coatings. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
5. Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBBs): A brominated flame retardant harmful to both humans and the environment. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
6. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs): A brominated flame retardant similar in toxicity to PBBs. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
7. Diisobutyl Phthalate (DIBP): Used as a plasticizer in PVC. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
8. Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP): Used in combination with other plasticizers for PVC components such as cables, sockets, pipes, and dampers. It is also found in paints, adhesives, sealants, and printing inks. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
9. Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP): Primarily used as a plasticizer in PVC. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
10. Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP): Used as a plasticizer in PVC. The allowable limit is ≤1000 ppm (0.1%).
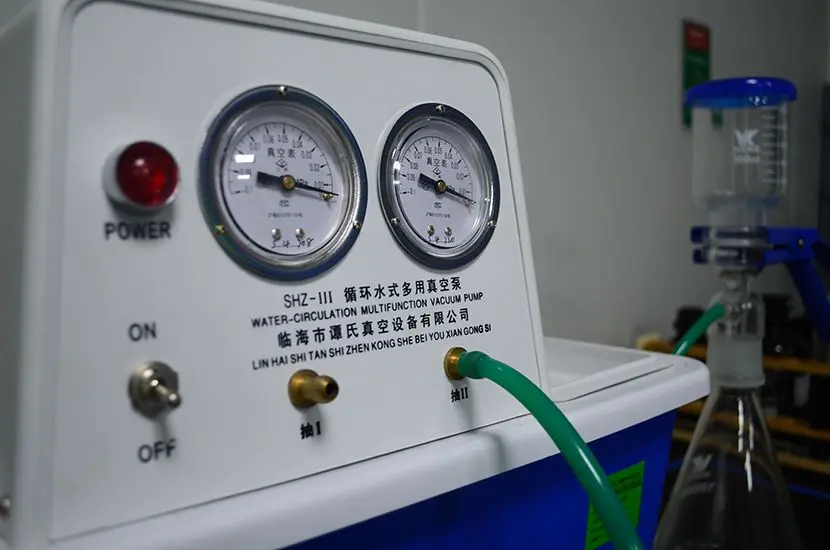
Testing Instruments for RoHS Ten Substances
- For Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), and Mercury (Hg): Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
- For Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI): Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometer (UV-Vis)
- For PBBs, PBDEs, DIBP, DBP, BBP, and DEHP: Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Irish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represent
Irish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represent
 Swedish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represe
Swedish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represe
 Amazon TIC Provider
Amazon TIC Provider
 Amazon Battery and Charger Requirements
Amazon Battery and Charger Requirements
 Amazon Japan METI A Domestic Administrator Service
Amazon Japan METI A Domestic Administrator Service
 What is "Amazon Japan PSE: A Domestic Adminis
What is "Amazon Japan PSE: A Domestic Adminis
 What Does "ASTM F963-17 Certified" Mean?
What Does "ASTM F963-17 Certified" Mean?
 ASTM F963 Board Games Compliance Testing
ASTM F963 Board Games Compliance Testing
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




