
Laptop Type-C EN IEC 62680-1-3 Certification Testing
Currently, charging port specifications for various electronic devices are inconsistent. This issue not only generates significant electronic waste, causing inconvenience for consumers, but also resULts in severe resource waste. To address this, the EU proposed revisions to the RED directive in 2019.
The EU has officially issued the revised directive Directive (EU) 2022/2380 regarding universal chargers. Starting from December 28, 2024 (for laptops, starting from April 28, 2026), all specified electronic products sold in EU member states must be equipped with USB Type-C charging ports conforming to the EN IEC 62680-1-3 standard and support fast-charging technology compliant with the EN IEC 62680-1-2 standard. Products that do not meet the EU universal charger standards after December 28, 2024 may face the risk of being phased out from the market.
Applicable Product Categories
- Handheld mobile phones
- Tablets
- Digital cameras
- Headphones
- Headsets (headphones with MICrophones)
- Handheld videogame consoles
- Portable speakers
- E-readers
- Keyboards
- Mice
- Portable navigation systems
- Earbuds
- Laptops (mandatory starting April 28, 2026)
Testing Requirements Explanation
01 Mandatory Condition: USB Type-C Charging Port
- Must meet the connector specifications and functional protocol specifications of EN IEC 62680-1-3.
02 PD Fast Charging Protocol
- If the product's charging voltage exceeds 5V, current exceeds 3A, or power exceeds 15W, the following requirements apply:
- Support and test compliance with the EN IEC 62680-1-2 PD fast charging protocol.
- Provide one test sample and a VIF file for the PD and functional protocol tests.
- Connector compliance proof can be provided by:
- Supplier test report for EN IEC 62680-1-3,
- AGC test report, or
- USB-IF TID certification.
03 Charger Decoupling
- Wireless communication devices sold in the EU may choose whether to include a charger. Instructions, packaging, or labels must specify charger type and configuration in a readable and visible format.
Testing Standards
EN IEC 62680-1-2:2022
"USB Power Delivery Specification"
- Defines a fast-charging protocol based on the CC channel in Type-C connectors.
- Enables power and device negotiation for voltage, current, and charging direction.
- Specifies electrical, physical layer, protocol layer, system policy, status reporting, and power rules.
EN IEC 62680-1-3:2022
"Type-C® Cable and Connector Specification"
- Covers Type-C connectors, cables, and protocols (Functional tests).
- Specifies pin definitions, mechanical structure, dimensional requirements, and electrical performance.
- Defines master-slave roles, power roles, power capabilities, handshake protocols, and state machines.
- Includes independent sections for USB4 support and Active Cable specifications.
Labeling Requirements
01 User Manual
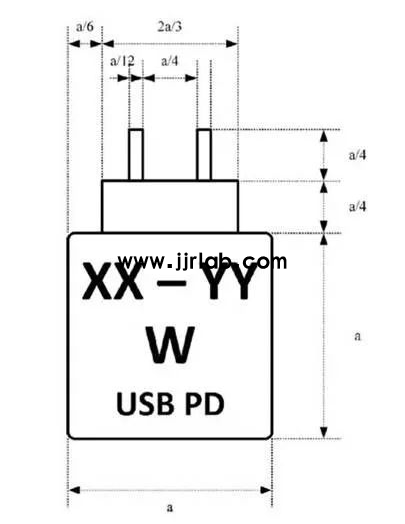
- Must indicate the power range required by the charging device:
“The power delivered by the charger must be between min [xx] Watts required by the radio equipment, and max [yy] Watts in order to achieve the maximum charging speed.”
02 Fast Charging Support
- Devices supporting fast charging must be labeled with "USB PD fast charging" and any other supported fast charging protocols.
03 Packaging Requirements
1. Packaging must indicate whether a charger is included.
2. Replace “XX” with the minimum power required by the device, and “YY” with the maximum power needed to achieve the fastest charging speed.
Example: The number determines the power the charger must deliver to achieve maximum speed.
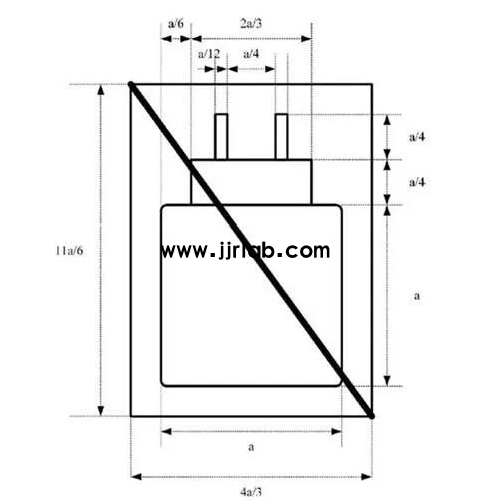
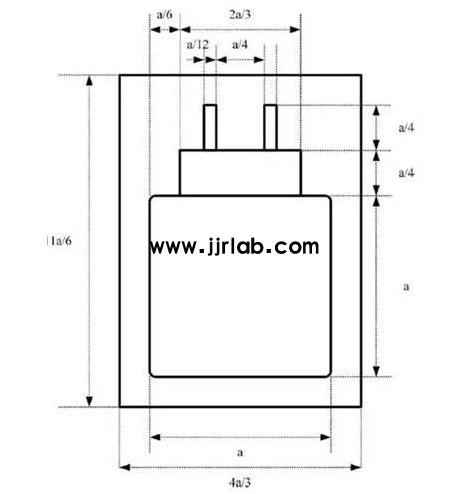
3. Dimensions:
- The label font height `a` should be at least 7mm, with proportional adjustments for scaling.
- Other visual elements (e.g., color, solid or hollow design, line thickness) may vary.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 How to get Australia SAA Compliance?
How to get Australia SAA Compliance?
 Does Canada Require RoHS Compliance
Does Canada Require RoHS Compliance
 EU CE LVD, EMC, RoHS Directives Compliance Guide
EU CE LVD, EMC, RoHS Directives Compliance Guide
 Quick Guide to the CE-LVD Low Voltage Directive
Quick Guide to the CE-LVD Low Voltage Directive
 Global Certification Guide for Lithium Batteries
Global Certification Guide for Lithium Batteries
 Compliance of Amazon 18650 Lithium Battery Product
Compliance of Amazon 18650 Lithium Battery Product
 What is CE Certification and EU Authorized Represe
What is CE Certification and EU Authorized Represe
 What Are the Lithium Battery Safety Tests?
What Are the Lithium Battery Safety Tests?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




