
METI and PSE Certification for Japanese Electrical
meti registration and pse certification
For Chinese electrical product manufacturers planning to export to Japan, METI registration and PSE certification are two indispensable hurdles. These two certifications are not only the "passes" for market access in Japan but also the core mechanisms to ensure product safety and protect consumer rights.
PSE Certification: Japan's Mandatory Certification
PSE Certification (Product Safety of Electrical Appliance & Materials) is a mandatory safety certification stipULated by Japan's Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Act (DENAN Act), aiming to ensure electrical products comply with Japanese safety standards. Based on risk levels, PSE certification is divided into two categories:
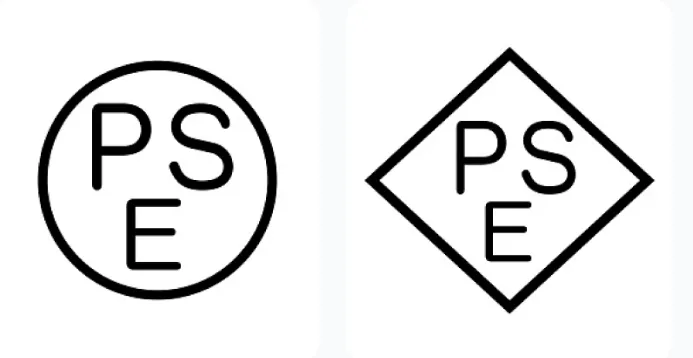
① Diamond PSE: Applies to 116 types of high-risk products (such as power plugs, electric heaters, transformers, etc.). It requires type tests by third-party institutions and factory inspections, with a validity period of 3-7 years, and the mark is a diamond shape.
② Round PSE: Covers 341 types of low-risk products (such as lamps, chargers, lithium batteries, etc.). It can be completed through self-declaration or third-party testing, with no fixed validity period, and the mark is a circle.
Certification Process
① Confirm product category: Determine whether the product falls under Diamond or Round PSE scope according to the DENAN Act catalog.
② Select a certification body: Diamond PSE requires testing by third-party institutions authorized by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI); Round PSE can be tested independently or entrusted to a third party.
③ Submit application documents: Including application form, product manual, difference declaration, list of key components, test report, etc.
④ Factory inspection (Diamond PSE only): Audit production processes, quality management system and environmental compliance.
⑤ Affix marks: After passing the certification, affix the corresponding pse mark on the product and packaging.
Core Test Items
① Safety tests: Insulation performance, withstand voltage test, leakage current, temperature rise, structural safety, etc.
② Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) tests: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), Electromagnetic Susceptibility (EMS), etc.
③ Special requirements: For example, lithium batteries must comply with JIS C 8712 or iec 62133 standards.
METI Registration
METI registration is a mandatory registration procedure for imported electrical products by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). It aims to establish a product traceability system to ensure market supervision is traceable and consumer safety is controllable. All products that have passed PSE certification (both Diamond and Round) must complete METI registration; otherwise, they cannot be sold legally.
Registration Subject and Responsibilities
① Registrant: Must be an importer or agent registeRED in Japan (overseas manufacturers need to entrust a local Japanese company to handle registration on their behalf).
② Responsibility division: Manufacturers bear product safety responsibilities, and importers are responsible for registration and market compliance.
Registration Process
Prepare materials:
① PSE certification certificate and test report
② Product manual (Japanese + English)
③ Importer's business license or registration certificate
④ Product photos, specifications, BOM list
⑤ Difference declaration (for series models)
Online submission: Fill in the application form and upload materials through the METI official website or authorized platform.
· Pay fees: Pay registration fees (approximately tens of thousands of yen) according to the product type.
Review and certification issuance: After METI approves the application, a registration number is issued, and product information is entered into a public database.
Key Notes
① Timeliness: Importers must complete registration within 30 days after the product arrives in Japan.
② Information changes: If there are changes to the company name, address or product model, re-registration is required.
③ Label requirements: The registration number must be marked on the product or packaging, and the format must comply with METI regulations.
The "Symbiotic Relationship" Between METI Registration and PSE Certification
Sequence: PSE first, METI follows
① Logical chain: Product testing → Obtain pse certificate → METI registration → Sale in Japanese market.
② Exception: If the product fails to pass PSE certification, even if METI registration is completed, it is still considered illegal sales.
Difference in responsible subjects
① PSE certification: Applied for by manufacturers or brand owners to prove product safety.
② METI registration: Handled by Japanese importers to establish a product traceability system.
Complementary legal effects
① PSE certification: Technical endorsement of product safety; products cannot enter the market without passing it.
② METI registration: Administrative license for market access; failure to register may result in fines or recall risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who is eligible to apply for METI registration?
· Only companies registered locally in Japan (importers) can apply for METI registration.
What is the validity period of METI registration?
· METI registration has no fixed validity period but needs to be updated along with the PSE certificate.
How to handle product changes?
· Any changes affecting product safety require re-PSE certification and METI registration.
How to select a certification body?
· A registered certification body with corresponding qualifications should be selected according to the product category.
METI registration and PSE certification constitute a dual guarantee system for Japan's electrical product market. China's JJR Laboratory provides METI registration and PSE certification services for electronic products entering the Japanese market, which can help enterprises save 40% of certification costs. Welcome to consult.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Is FCC Testing Required?
Is FCC Testing Required?
 Where to Find FCC Test Reports
Where to Find FCC Test Reports
 LFGB Compliance Testing for Plastic Food Contact M
LFGB Compliance Testing for Plastic Food Contact M
 How to get LFGB Compliance Report for Food Grade P
How to get LFGB Compliance Report for Food Grade P
 LFGB Certification Process for Kitchenware Product
LFGB Certification Process for Kitchenware Product
 LFGB Test Requirements for Food Contact Materials
LFGB Test Requirements for Food Contact Materials
 Irish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represent
Irish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represent
 Swedish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represe
Swedish Battery Act Requires an Authorised Represe
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




