
What is ESD Compliance Testing?
What is ESD?
ESD stands for Electrostatic Discharge, referring to the sudden flow of electricity between two objects with different electrical potentials. This occurs when static electricity builds up on one object and contacts another with a different potential.
ESD can arise from various sources, such as friction, air movement, or contact with other objects. It is common in daily life and can damage electronic components, particULarly those sensitive to electrostatic discharge.
The effects of ESD range from barely noticeable minor shocks to more severe discharges that can cause permanent damage to electronic devices. This is especially problematic in environments where electronic components are manufactuRED, handled, or transported.
To prevent damage caused by ESD, measures like using anti-static mats, wrist straps, and other protective equipment are employed. Additionally, ESD Testing is conducted to assess a device's ability to withstand and dissipate electrostatic discharge.
What is esd testing?
ESD testing (electrostatic discharge testing) evaluates an electronic device's capability to withstand and dissipate electrostatic discharges. This procedure typically involves subjecting the device to high-voltage discharges through contact or air and measuring the resulting current and voltage. The device's performance is assessed based on whether it continues to function properly after the discharge.
ESD testing is critical during product development for electronic devices, especially those sensitive to ESD, to ensure they can handle real-world static events and comply with safety and performance regulations.
Common ESD Testing Standards
Various industry standards guide ESD testing, including:
- iec 61000-4-2 (International Electrotechnical Commission): Evaluates ESD immunity.
- ANSI/ESD S20.20 (American National Standards Institute): Establishes ESD control program requirements.
- MIL-STD-883 (U.S. Department of Defense): Includes methods for military-grade electronics testing.
- JEDEC JESD22-A114 and JESD22-C101: Assess robustness of integrated circuits to HBM and MM discharges.
- GB/T 19951-2019 (China National Standard): Defines ESD testing for electronic devices.
- ISO 10605-2008 (International Organization for Standardization): Tests ESD immunity, widely accepted in the electronics industry.
Methods of ESD Testing
The appropriate ESD testing method depends on the type of device being tested and the applicable industry standards. Common methods include:
● Human Body Model (HBM)
Simulates the discharge that might occur when a person touches electronic equipment. High-voltage pulses are released through a human body simulator to test sensitivity.
● Machine Model (MM)
Replicates discharges that could happen when electronic devices come into contact with manufacturing equipment. This tests device robustness.
● Charged Device Model (CDM)
Simulates discharges during handling or assembly by releasing high-voltage pulses from charged devices like IC packages. This method tests device sensitivity.
● IEC 61000-4-2
Uses a probe to release high-voltage pulses to simulate ESD events that occur during the exposure of devices to electrostatic discharges. It assesses ESD immunity.
In all testing methods, devices are evaluated based on whether they continue functioning normally post-discharge. Results are compared to industry standards to determine compliance.
ESD Testing Standards
● IEC 61000-4-2
An IEC standard that outlines procedures for assessing the ESD immunity of electronic devices. It applies to all types of electronics and includes test levels ranging from 2 kV to 15 kV, simulating different real-world ESD events. The test involves discharging high-voltage pulses into the device and comparing performance with defined criteria to determine compliance.
● ANSI/ESD S20.20
An ANSI standard providing guidelines for ESD control programs to protect electronics during manufacturing, handling, and use. Key aspects include:
- ESD Protected Areas (EPA): Defined zones where ESD-sensitive items are handled.
- Grounding: All conductive materials in the EPA must be grounded.
- Personnel Grounding: Workers in the EPA must use wrist straps or other grounding devices.
- ESD Protective Packaging: Sensitive items must be packaged using protective materials like static shielding bags.
- Control Procedures: Procedures to minimize ESD damage risks must be implemented and followed.
This standard is widely recognized for establishing reliable ESD control methods.
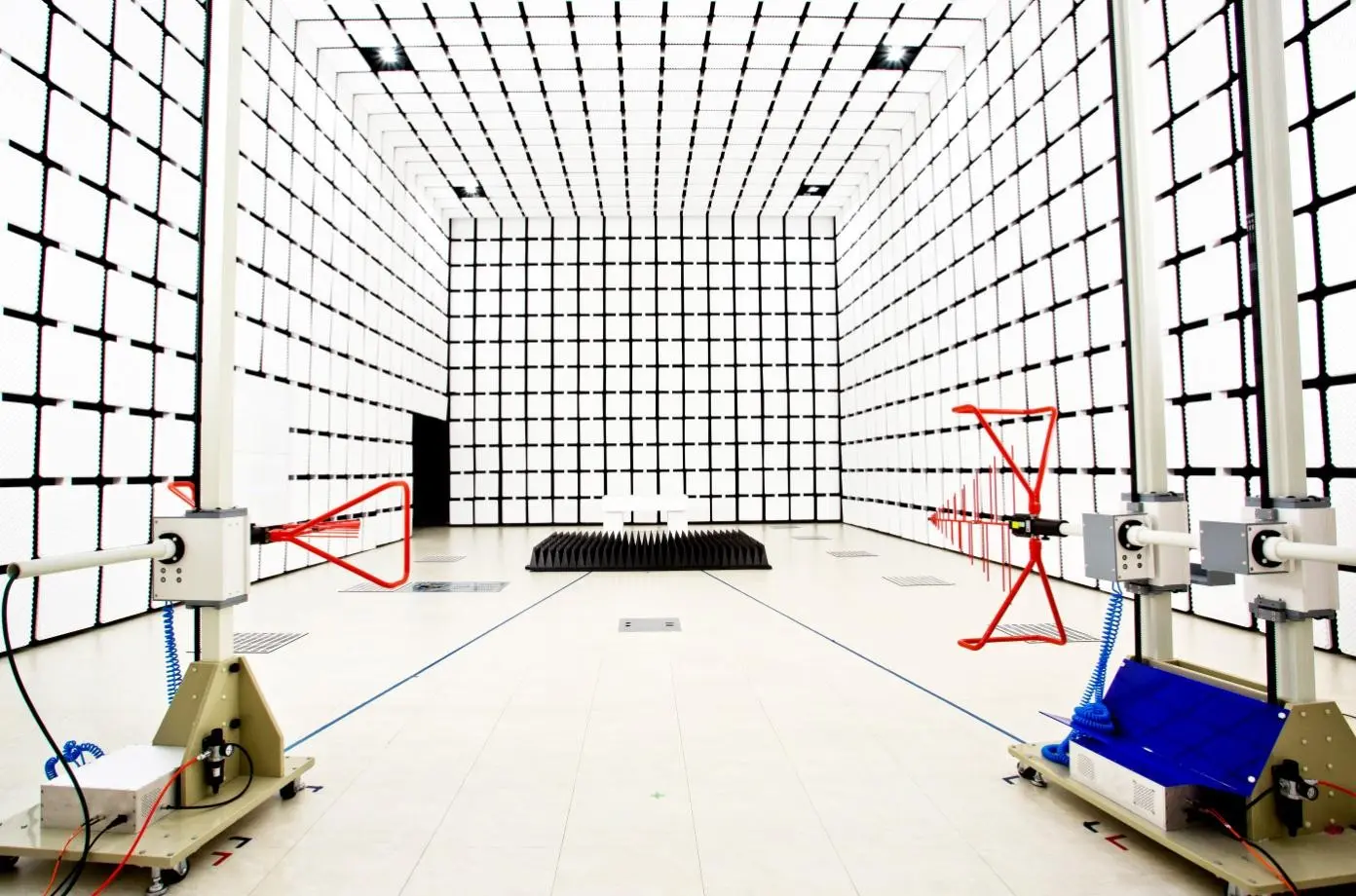
ESD Testing Equipment
Specialized equipment is used to generate and measure electrostatic discharges during testing. Examples include:
- ESD Guns: Handheld devices that simulate ESD events by producing static discharge pulses.
- Electrostatic Discharge Simulators: Desktop devices that generate discharge pulses for testing.
- HBM and MM Simulators: Devices designed specifically to produce pulses for HBM and MM testing.
- Charge Plate Monitors: Measure static charges on surfaces like floors or workstations to ensure proper grounding.
- ESD Testers: Combine multiple testing functions into one device.
- ESD Workstations: Designed to minimize risks of ESD damage during handling and assembly of electronics.
These devices are crucial for accurately simulating and measuring ESD events to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and real-world conditions.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
Canada ISED Certification RSS-247 Standard Testing
 What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
What Are the Product Compliance for Amazon Austral
 Australia IoT Security Compliance
Australia IoT Security Compliance
 V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
V16 Warning Light EU EN 18031 Cybersecurity Certif
 Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
Japan IoT Security JC-STAR Certification
 FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
FCC SDoC Compliance Information Statement
 What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
What Does FCC SDoC Certification Mean?
 What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
What is Bisphenol A (BPA) Testing?
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




