
JIS C 62368-1 Electrical Safety Testing Standard
Japan’s pse certification (Product Safety Electrical Appliance & Materials) is a mandatory safety certification for electrical and electronic products entering the Japanese market. Among relevant standards, JIS 62368-1 (aligned with IEC 62368-1) serves as the core safety standard for Information Technology Equipment (ITE) and Audio-Visual (AV) Equipment, replacing the previous standards J 60950-1 (for ITE) and J 60065 (for AV).
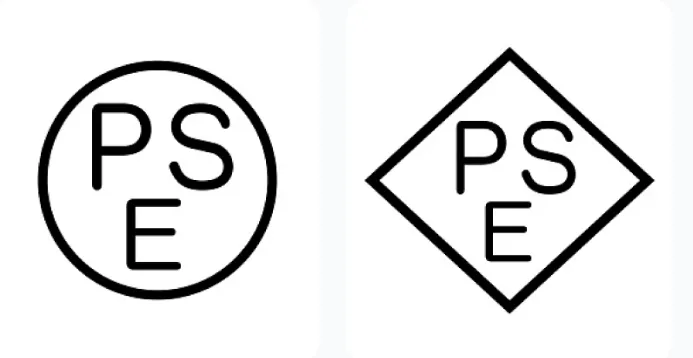
1. Two Types of PSE Certification
Japan’s PSE Certification is divided into two categories, applicable to different product ranges:
Certification Type | Applicable Products | Testing Standards | Certification Method |
Diamond PSE (Mandatory) | High-risk products (e.g., power adapters, lithium batteries) | JIS C 62368-1 + Specific Product Standards | Registration with Japan’s METI + Testing by Designated Laboratories |
CircULar PSE (Self-Declaration) | Low-risk products (e.g., computers, monitors) | JIS C 62368-1 | Self-testing by Manufacturers + Technical Document Retention |
Notes:
① Diamond PSE products must be tested by Japan-accREDited laboratories (e.g., JET, JQA, UL Japan) to obtain certification.
② Circular PSE compliance can be self-verified by manufacturers, but test reports must be retained for inspection purposes.
2. Core Requirements of JIS C 62368-1 (Based on IEC 62368-1)
(1) Safety Philosophy (Hazard-Based Engineering, HBE)
The standard adopts energy source classification (Class 1/2/3) and protective measures (PS1/PS2/PS3) to assess product risks, with key focus on the following aspects:
① Electric Shock Protection: Insulation, grounding, and safety clearance
② Fire Prevention: Enclosure flame retardant rating, overcurrent protection
③ Thermal Injury Prevention: Temperature rise testing, abnormal operating condition simulation
④ Mechanical Injury Prevention: Product stability, sharp edge protection
(2) Key Testing Items
Testing Category | Specific Requirements |
Electrical Safety | Dielectric withstand voltage test (AC 1500V/1min), leakage current measurement, grounding resistance test |
Energy Hazard Control | Voltage/current limits for accessible terminals (in line with Class 1/2/3 classification) |
Fire Protection | Flame retardancy of non-metallic materials (e.g., UL94 V-0 rating), PCB fire resistance |
Battery Safety | Lithium batteries must comply with JIS C 8712 (Japan’s local standard) |
Marking & Documentation | Mandatory inclusion of Japanese warning statements and pse mark |
3. PSE Certification Process
(1) Diamond PSE Certification Process (Taking Power Adapters as an Example)
1. Determine Applicable Standards: Confirm that the product falls under the scope of "Specified Electrical Appliances" (Diamond PSE) as defined by Japan’s Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Act.
2. Testing Preparation:
① Provide product samples, circuit diagrams, and BOM lists (key components must meet JIS standards).
② Select a Japan-accredited laboratory (e.g., consult JJR LAB).
3. Testing & Reporting:
① Conduct safety testing in accordance with JIS C 62368-1.
② Additional testing per JIS C 8712 is required for lithium battery products.
4. meti registration: Complete registration with Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) to obtain the pse certificate.
5. Product Marking: The product must be labeled with the Diamond PSE mark + registration number (e.g., PSE123456).
(2) Circular PSE Certification Process (Taking Monitors as an Example)
1. Self-Compliance Assessment: Manufacturers conduct self-testing or entrust laboratories to verify compliance with JIS C 62368-1.
2. Technical Document Retention: Test reports and risk assessment documents must be retained for 10 years.
3. Product Marking: Label the product with the Circular PSE mark; no registration number is required.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are JIS C 62368-1 and IEC 62368-1 identical?
Their technical content is consistent, but Japan may add localized requirements (e.g., Japanese-language labeling, lithium battery standards per JIS C 8712).
Q2: Can products with existing CCC or CE certification be directly converted to PSE certification?
Partial test results can be reused (e.g., insulation, fire protection tests), but the following supplementary steps are required:
① Prepare Japanese-language manuals and labels
② Ensure compliance with JIS C 8712 (for lithium battery products)
③ Conduct testing via Japan-accredited laboratories for Diamond PSE certification
Q3: What is the validity period of PSE certification?
① Diamond PSE: 5 years (regular renewal is required)
② Circular PSE: No fixed validity period, but technical documents must be retained for inspection.
Certification Optimization Tips:
1. Plan Certification Path in Advance: Confirm whether the product falls under Diamond PSE or Circular PSE (refer to the product list on METI’s official website).
2. Localization Adaptation: Ensure labels and manuals meet Japanese Consumer Law requirements; use Japan-standard two-pin flat plugs for power connections.
3. Key Component Selection: Prioritize components with existing PSE certification (e.g., power supplies, batteries).
4. Test Cost Optimization: Reuse existing IEC 62368-1 test results to reduce redundant testing and save costs.
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 2026 EU SVHC Candidate List (253 Substances)
2026 EU SVHC Candidate List (253 Substances)
 LFGB Certification Cost and Timeline Guide
LFGB Certification Cost and Timeline Guide
 Bluetooth FCC Test Report
Bluetooth FCC Test Report
 Is FCC Testing Required?
Is FCC Testing Required?
 Where to Find FCC Test Reports
Where to Find FCC Test Reports
 LFGB Compliance Testing for Plastic Food Contact M
LFGB Compliance Testing for Plastic Food Contact M
 How to get LFGB Compliance Report for Food Grade P
How to get LFGB Compliance Report for Food Grade P
 LFGB Certification Process for Kitchenware Product
LFGB Certification Process for Kitchenware Product
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




