
RCM Certification Electrical Equipment
Introduction to rcm certification
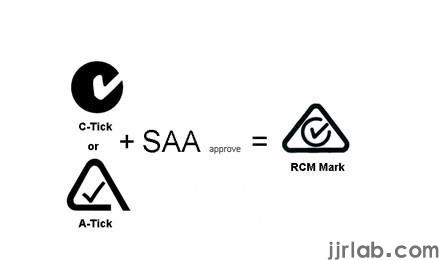
RCM certification, also known as 'RegULatory Compliance mark,' is a safety and electromagnetic compatibility certification mark for electrical equipment and systems in Australia and New Zealand. It is a mandatory certification replacing the previous SAA and c-tick certifications. All electrical equipment and systems sold in Australia and New Zealand must undergo RCM certification to be legally sold.
Significance of RCM Certification
1. Consumer Protection: RCM certification ensures that electrical equipment and systems comply with safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards, ensuring consumer safety during product use.
2. Enhanced Market Competitiveness: Products certified through RCM gain recognition in the Australian and New Zealand markets, enhancing market competitiveness.
3. Environmental Protection: RCM certification also considers the environmental performance of products by limiting electromagnetic radiation to protect the environment.
4. Facilitation of International Trade: Products certified through RCM can be sold in global markets, facilitating international trade.
RCM Certification Process
1. Understanding Regulations: You need to understand the electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility regulations in Australia and New Zealand. These regulations are issued by Australian certification bodies (e.g., Australian RCM Certification) and are published in government gazettes, with detailed descriptions provided in specific product catalogs such as lighting fixtures.
2. Determining Product Scope: Based on product catalogs and relevant regulations, determine whether your product requires RCM certification. Both regulated and non-regulated products, such as those falling under Hazardous Risk Category 61, require registration. Note that the EESS system has been effective since March 1, 2013, requiring products to be registeRED in the EESS database and bear the rcm mark to be sold in the market.
3. Selecting Certification Bodies: You can choose CHINA JJRLAB Laboratory (hello@jjrlab.com) for assessment and testing or engage local third-party certification bodies in Australia. When selecting a certification body, ensure they have sufficient experience and qualifications to guarantee the accuracy and effectiveness of testing.
4. Submitting Application: After selecting a certification body, submit a certification application, providing basic product information, test reports, manuals, and other relevant documents.
5. Conducting Testing: The certification body will test your product based on regulations and the information you provided. During testing, the certification body will assess the product's safety and electromagnetic compatibility.
6. Document Review: The certification body will review the documents and test reports you provided to ensure compliance with regulations and product standards.
7. Issuing Certificate: If the document review and testing pass, the certification body will issue an rcm certificate for your product. The certificate will include information such as the product model, serial number, and certification body.
8. Product Registration: You need to register your product in the EESS database and affix the RCM mark. Only then can your product be legally sold in the Australian and New Zealand markets.
rcm certification costs
It should be noted that the cost of RCM certification varies depending on the specific circumstances of the enterprise and is not a fixed amount. Factors such as the scale of the enterprise, industry sector, and scope of certification can affect the cost. Generally, RCM certification costs include application fees, on-site audit fees, certification decision fees, and annual audit fees.
According to relevant data, the RCM certification costs for small and medium-sized enterprises typically range from $5000 to $15000. For large enterprises, certification costs may be higher, exceeding $20000. This is because large enterprises require more resources for certification implementation and maintenance. Additionally, the reputation and professionalism of the certification body also affect costs. Well-known certification bodies may charge higher fees due to their higher market visibility and recognition. However, they can provide more reliable certification services, ensuring the authority and credibility of the certification results.
Scope of RCM Certification
Australia and New Zealand enforce mandatory RCM certification for electronic and electrical products, including telecommunications products, radio communication products, electrical products, and electromagnetic compatibility. During the RCM certification process, products need to undergo laboratory assessment, testing, issuance of test reports, and submission of relevant documents to Australian certification bodies for review and approval before obtaining the RCM certificate. Some non-regulated electronic and electrical products do not require registration, but only Level 3 electrical products need registration. RCM certification replaces the previous SAA, C-Tick, and A-Tick certification requirements, serving as a regulatory compliance mark applicable to electrical products in Australia and New Zealand.
Common Questions About RCM Certification
Can factories apply for RCM certification themselves?
No, RCM certification is a certification model that requires an Australian company as a guarantor, so Chinese factories cannot directly hold RCM certificates.
What should be done if there are modifications to RCM-certified products?
Any modifications to certified products must be reported to the certification body, and retesting and updating of certification may be required.
What should certification bodies pay attention to when handling product certification?
Certification bodies need to ensure that products comply with all relevant regulations and technical requirements and update certification information promptly to maintain validity."
Email:hello@jjrlab.com
Write your message here and send it to us
 EMC Item – Introduction to Radiated Emission Test
EMC Item – Introduction to Radiated Emission Test
 IEC 62471 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp
IEC 62471 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp
 New European Toy Standard EN 71-1:2026
New European Toy Standard EN 71-1:2026
 EN71 Series Standards Compliance February 13, 2026
EN71 Series Standards Compliance February 13, 2026
 European Toy Safety Standard EN 71-20:2025
European Toy Safety Standard EN 71-20:2025
 EN 18031 Certification for Connected Devices on Am
EN 18031 Certification for Connected Devices on Am
 Compliance Guide for Portable Batteries on Amazon
Compliance Guide for Portable Batteries on Amazon
 2026 EU SVHC Candidate List (253 Substances)
2026 EU SVHC Candidate List (253 Substances)
Leave us a message
24-hour online customer service at any time to respond, so that you worry!




